A land parcel map is a visual representation of a specific area of land that has been divided into individual parcels.
These maps are used to define the boundaries of each parcel and provide information about the size and shape of the land.
They are an essential tool for land surveyors, real estate professionals, and government officials who need to know the exact location and dimensions of a piece of land.

Land parcel maps can be created using a variety of methods, including aerial photography, satellite imagery, and ground surveys.
The maps typically include information about the location of roads, buildings, and other features that may be relevant to the use and development of the land.
They may also include information about zoning regulations, environmental restrictions, and other legal considerations that may impact the use of the land.
Understanding the information contained in a land parcel map is essential for anyone involved in buying, selling, or developing land.
Table of Contents
Definition of a Land Parcel Map
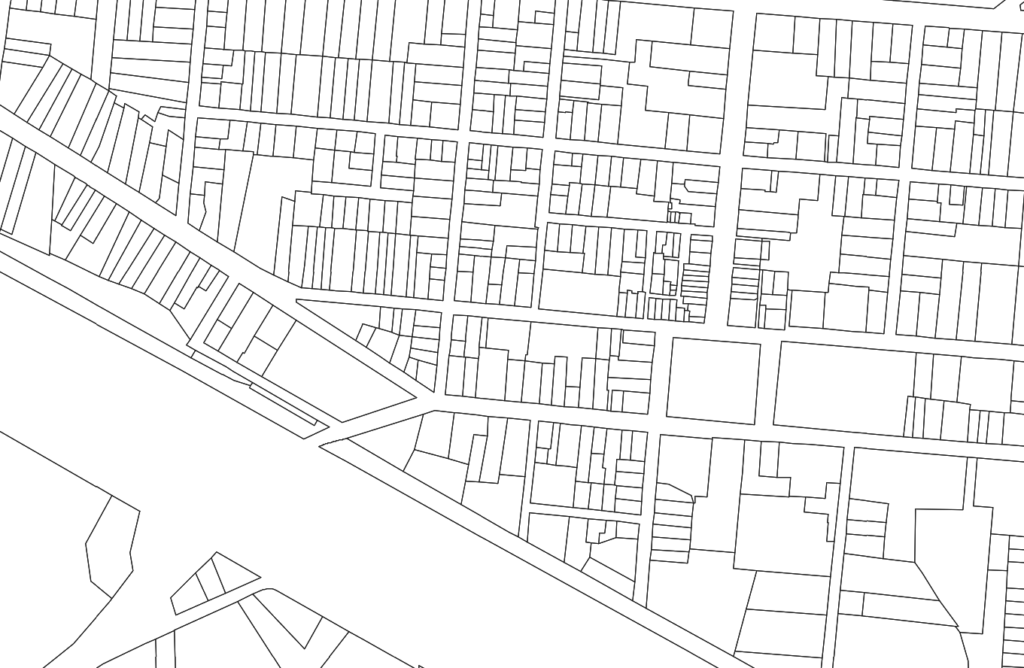
A land parcel map is a visual representation of a piece of land that shows the boundaries, dimensions, and other relevant information about the parcel.
It is a valuable tool for landowners, developers, and government officials who need to understand the characteristics of a particular piece of land.
Land parcel maps are typically created by surveyors or other professionals who use specialized equipment to accurately measure the boundaries of a piece of land.
The information gathered during this process is then used to create a detailed map that shows the boundaries of the parcel, as well as any structures, roads, or other features that may be present on the land.
Land parcel maps can be used for a variety of purposes, including property assessments, land use planning, and zoning.
They are also commonly used by real estate professionals to help buyers and sellers understand the characteristics of a particular piece of land.
In order to be effective, a land parcel map must be accurate, up-to-date, and clearly labeled.
It should include information about the size and shape of the parcel, as well as any easements, rights-of-way, or other encumbrances that may affect the use of the land.
Components of a Land Parcel Map
A land parcel map is a graphical representation of a piece of land that shows its boundaries, dimensions, and other features.
A land parcel map is created by a surveyor using a variety of tools and techniques to accurately measure and document the physical features of a piece of land.
The following are the key components of a land parcel map:
Boundaries and Lot Lines
The boundaries and lot lines of a parcel are the most important components of a land parcel map.
These lines define the extent of the parcel and are used to determine the property’s size and shape.
The boundaries are typically marked by physical features such as fences, walls, or natural features like rivers or streams.
The lot lines are the lines that divide the parcel into smaller sections, which are often used for zoning and land use purposes.
Parcel Identification Numbers
Each parcel of land is assigned a unique identification number, which is used to identify the property for legal, tax, and other purposes.
This number is typically included on the land parcel map and is used to link the map to other documents related to the property.
Scale and Orientation
The scale of a land parcel map refers to the ratio of the size of the map to the actual size of the land.
The scale is important because it determines the level of detail that can be shown on the map.
The orientation of the map refers to the direction in which the map is facing, and is determined by the surveyor based on the location of the parcel and other factors.
Topographic Features
A land parcel map may also include topographic features such as elevation contours, water bodies, and vegetation.
These features provide additional information about the physical characteristics of the land and can be useful for planning and development purposes.
Purpose and Uses
A land parcel map is a graphical representation of a property’s boundaries and other relevant information.
The purpose of a land parcel map is to provide a clear and accurate picture of the land’s boundaries, dimensions, and location.
The map is used for various purposes, including property ownership, land use planning, legal documentation, zoning and regulation compliance.
Property Ownership
Land parcel maps are used to establish and verify property ownership.
The map shows the exact location and boundaries of the property, which helps to avoid disputes over property lines.
Property owners can also use the map to determine the size and shape of their property, which is useful for planning and development purposes.
Land Use Planning
Land parcel maps are used in land use planning to identify areas suitable for development and conservation.
The map provides information on the land’s topography, soil type, and other features, which helps planners to determine the best use of the land.
The map is also used to identify areas that are environmentally sensitive and should be protected from development.
Legal Documentation
Land parcel maps are used in legal documentation to establish property boundaries and ownership.
The map is used in property transactions, such as sales and leases, to ensure that the parties involved understand the exact location and size of the property.
The map is also used in legal disputes over property boundaries and ownership.
Zoning and Regulation Compliance
Land parcel maps are used to ensure compliance with zoning and other regulations.
The map shows the location and boundaries of different zoning districts, which helps property owners to understand the permitted uses and restrictions for their property.
The map is also used to identify areas that are subject to environmental regulations, such as wetlands and floodplains.
Creation Process

Creating a land parcel map involves several steps, including surveying techniques, data collection, and map drawing and design.
Each of these steps is crucial in ensuring that the map accurately represents the land parcels in question.
Surveying Techniques
Surveying techniques are used to accurately measure the boundaries of land parcels.
This involves using specialized equipment, such as total stations and GPS receivers, to measure distances and angles.
Surveyors also use techniques such as triangulation and traverse to establish control points and measure the boundaries of the land parcels.
Data Collection
Once the boundaries of the land parcels have been established, data collection can begin.
This involves collecting information about the land parcels, such as the size and shape of each parcel, the location of any buildings or structures on the parcels, and any other relevant information.
Data can be collected using a variety of methods, including aerial photography, satellite imagery, and ground-based surveys.
Map Drawing and Design
Once the surveying and data collection are complete, the land parcel map can be drawn and designed.
This involves using specialized software to create a digital map of the land parcels, including all of the relevant data that was collected during the surveying and data collection phases.
The map must be designed in a way that is clear and easy to read, with all of the relevant information clearly labeled and organized.
Types of Land Parcel Maps
There are various types of land parcel maps that serve different purposes and are created using different methods. Here are three common types of land parcel maps:
Assessor’s Maps
Assessor’s maps are created by local government agencies and are used for property tax assessment purposes.
These maps show the boundaries of individual properties and include information such as parcel numbers, lot sizes, and assessed values.
Assessor’s maps are typically updated annually to reflect changes in property ownership and value.
Cadastral Maps
Cadastral maps are used for land ownership and management purposes.
They show the boundaries of individual parcels of land, as well as details such as land use, zoning, and easements.
Cadastral maps are created by government agencies such as the Bureau of Land Management and are used by landowners, surveyors, and other professionals involved in land management.
GIS-Based Parcel Maps
GIS-based parcel maps are created using geographic information system (GIS) technology.
These maps are highly detailed and can include a wide range of information, such as property boundaries, topography, aerial imagery, and environmental data.
GIS-based parcel maps are used by a variety of professionals, including urban planners, environmental scientists, and real estate developers.
Reading a Land Parcel Map

A land parcel map is a visual representation of land that is used by surveyors, real estate agents, and local government officials to determine land ownership, property boundaries, and other important information.
Reading a land parcel map can be intimidating for those who are not familiar with the symbols and legends used on the map. This section will provide an overview of how to read and interpret a land parcel map.
Understanding Symbols
Land parcel maps use a variety of symbols to convey important information about the land.
Some common symbols include:
- Lines: Lines on a land parcel map represent property boundaries.
Solid lines indicate actual property lines, while dotted lines indicate proposed property lines. - Numbers: Numbers on a land parcel map represent the size of the property in acres or square feet.
- Arrows: Arrows on a land parcel map indicate the direction of the property lines.
- Squares: Squares on a land parcel map represent buildings or structures on the property.
- Circles: Circles on a land parcel map represent wells or other water sources on the property.
Interpreting Legends
Legends on a land parcel map provide additional information about the symbols used on the map.
The legend will typically include a list of symbols and their meanings. It may also include information about the scale of the map, the date of the survey, and other important details.
When interpreting a legend, it is important to pay attention to the scale of the map.
The scale will indicate the relationship between the size of the map and the actual size of the land.
For example, a map with a scale of 1:10,000 means that one inch on the map represents 10,000 inches (or 833.33 feet) on the ground.
Challenges in Mapping

Inaccuracies and Errors
Land parcel mapping is a complex process that involves collecting and analyzing a significant amount of data.
However, even with the use of advanced technology, inaccuracies and errors can occur during the mapping process.
These inaccuracies can be caused by a variety of factors, such as human error, outdated data, and the limitations of the technology being used.
One common source of inaccuracies in land parcel mapping is the use of outdated or incomplete data.
For example, if a map is based on data that is several years old, it may not accurately reflect changes that have occurred on the ground since that time.
Additionally, if the data used to create the map is incomplete or inaccurate, this can also lead to errors in the final product.
Another source of inaccuracies in land parcel mapping is the limitations of the technology being used.
For example, satellite imagery may not be able to capture certain features on the ground, such as small buildings or trees.
Additionally, the accuracy of GPS data can be affected by factors such as atmospheric conditions and interference from other electronic devices.
Updating and Maintenance
Another challenge in land parcel mapping is keeping the maps up-to-date and maintaining their accuracy over time.
As the landscape changes, new buildings are constructed, and old ones are torn down, it is important to update the maps to reflect these changes.
However, this can be a time-consuming and expensive process.
In addition to the cost and time required to update land parcel maps, there are also challenges associated with maintaining their accuracy over time.
For example, if a map is not updated regularly, it may become outdated and inaccurate.
Additionally, if the data used to create the map is not maintained properly, it may become corrupted or lost over time.
Technological Advancements
Digital Mapping Tools
With the advent of digital mapping tools, land parcel mapping has become more efficient and accurate.
Digital tools such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS) allow land surveyors to create and manage land parcel maps with ease.
GIS software enables surveyors to overlay various data sets on top of each other to create a comprehensive view of the land.
This technology also allows for the creation of 3D maps, which provide a more realistic representation of the land.
In addition to GIS software, other digital mapping tools such as GPS and laser scanners have also made land parcel mapping more accurate.
GPS technology allows surveyors to pinpoint the exact location of boundaries and other features on the land.
Laser scanners, on the other hand, can create highly detailed 3D models of the land, which can be used to create accurate and detailed maps.
Satellite Imagery and Aerial Photography
Satellite imagery and aerial photography have also revolutionized land parcel mapping.
High-resolution satellite images and aerial photographs provide surveyors with a bird’s eye view of the land, which can be used to create accurate and detailed maps.
These images can also be used to identify changes in the land over time, such as changes in vegetation or the construction of new buildings.
In addition to traditional satellite imagery and aerial photography, new technologies such as drones have also been used for land parcel mapping.
Drones can capture high-resolution images and videos of the land from various angles, which can be used to create detailed 3D models of the land.
This technology has made land parcel mapping more accessible and affordable for smaller surveying firms.
Overall, technological advancements have made land parcel mapping more efficient, accurate, and accessible.
With the use of digital mapping tools, satellite imagery, and aerial photography, surveyors can create detailed and comprehensive maps of the land, which can be used for a variety of purposes.
